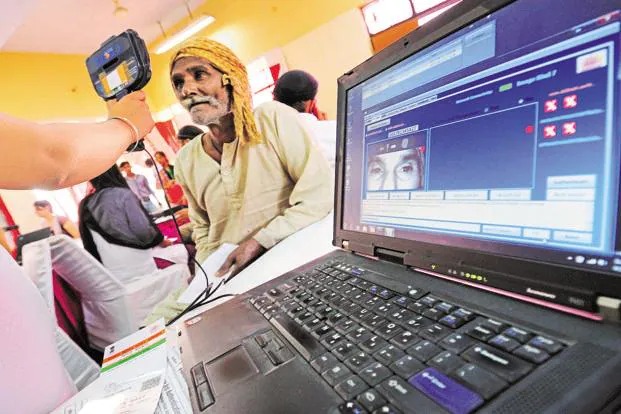
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has achieved a remarkable milestone with its AI-powered Aadhaar Face Authentication system, recording over 130.5 crore transactions since its launch in October 2022. This transformative technology is reshaping biometric verification in India, offering enhanced security, convenience, and accessibility across sectors. With its rapid adoption and integration into private and public services, Aadhaar Face Authentication is setting new benchmarks for digital identity systems globally.
Key Points of the Achievement
Record Transactional Growth:
More than 78% of the total transactions were made in the year 2024-25 alone, with around 102 crore valid authentications made within that single year.
Between January and March 2025, a record 39.5 crore transactions were registered, reflecting the increasing usage and effectiveness of the system.
AI-Driven Biometric Technology:
The system incorporates cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms for safe and touchless authentication.
It overcomes issues such as low-quality fingerprints, making it inclusive for those who may have trouble with conventional biometric processes.
Widespread Adoption Across Industries:
Aadhaar Face Authentication is used by more than 102 organizations across fintech, telecom, healthcare, and e-commerce industries.
Government welfare schemes such as PM Awas Yojana (Urban) and PM-Kisan have incorporated this technology to make benefit disbursal easier.
Accessibility with Ease of Use
Both Android and iOS platforms are supported by the system, providing hassle-free access to services for Aadhaar holders.
It facilitates "anytime, anywhere" authentication without the need for physical documents or personal verification.
Revolutionizing Governance and Service Delivery
The Aadhaar Face Authentication system is transforming governance by increasing transparency and efficiency in service delivery. By removing fraud and duplication in welfare schemes, it ensures that benefits reach the targeted beneficiaries. For instance:
Government Initiatives: Initiatives such as PM-Kisan employ face recognition to authenticate beneficiaries' identities prior to disbursal of funds.
Banking & Finance: Banks are utilizing this technology for customer sign-up, loan approvals, as well as e-KYC processes.
Healthcare: Hospitals are employing biometric authentication for patient registration and secure access to medical records.
Private Sector Integration: A New Frontier
In a policy change of major importance, the Indian government has permitted private organizations to incorporate Aadhaar Face Authentication within their solutions. This action has followed the issue of the Aadhaar Authentication for Good Governance Amendment Rules, 2025. Important features are:
Increased Use Cases:
Private companies operating in industries such as hospitality, education, credit rating, and e-commerce are now able to employ face authentication for purposes such as customer onboarding, attendance tracking for employees, and exam enrollments.
Simplified Processes:
The Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) has initiated an online portal to assist private organizations in the integration process.
Improved Security Features:
The new framework comprises regulatory mechanisms to handle privacy issues highlighted by previous Supreme Court judgments regarding Aadhaar usage by private companies.
Benefits of Aadhaar Face Authentication
Improved Security:
Biometric information such as facial recognition is specific to every individual, minimizing identity theft or fraud risks.
Convenience:
Users do not have to memorize passwords or keep physical documents; a mere facial scan is enough.
Inclusivity:
The system supports users with low-quality fingerprints due to age or physically demanding jobs.
Fraud Prevention:
Biometric characteristics are hard to replicate or counterfeit, thus guaranteeing that only legitimate users can access services.
Multimodal Capabilities:
The use of facial recognition in conjunction with other biometric techniques such as fingerprints adds an extra layer of security.
Challenges and Privacy Concerns
Though Aadhaar Face Authentication has many advantages, it also poses legitimate concerns:
Data Security Risks:
Biometric data stored centrally is susceptible to cyberattacks. Previous breaches of Aadhaar-related information have pointed to these risks.
Privacy Issues:
Opponents claim that broadening the scope of Aadhaar to private companies might result in unauthorized surveillance or abuse of personal information.
Exclusion Risks:
Facial recognition systems prone to errors can miss identifying people, potentially denying them vital services.
Legal Safeguards:
India's data protection legislation is in the process of evolving, with gaps remaining in dealing with privacy breaches effectively.
Future Prospects
The success of Aadhaar Face Authentication opens the door to more innovation in biometric authentication:
UIDAI is developing improvements in other biometric modalities such as fingerprints and iris scans through benchmarking challenges.
The addition of AI-based features to India's Central KYC Registry will further enhance digital identity infrastructure.
Ongoing advances in liveness detection technologies will aid in fighting novel threats such as deepfakes.
Conclusion
The milestone of more than 130.5 crore transactions is a testament to the revolutionary potential of Aadhaar Face Authentication in creating a digitally empowered society. Through the application of state-of-the-art AI/ML technologies, UIDAI has not only improved service delivery but also set an international benchmark for digital identity systems. But privacy issues and strong legal frameworks will be important as India goes further on its path toward a completely digitized future.
Sources: Economic Times, Devdiscourse, Mobile ID World