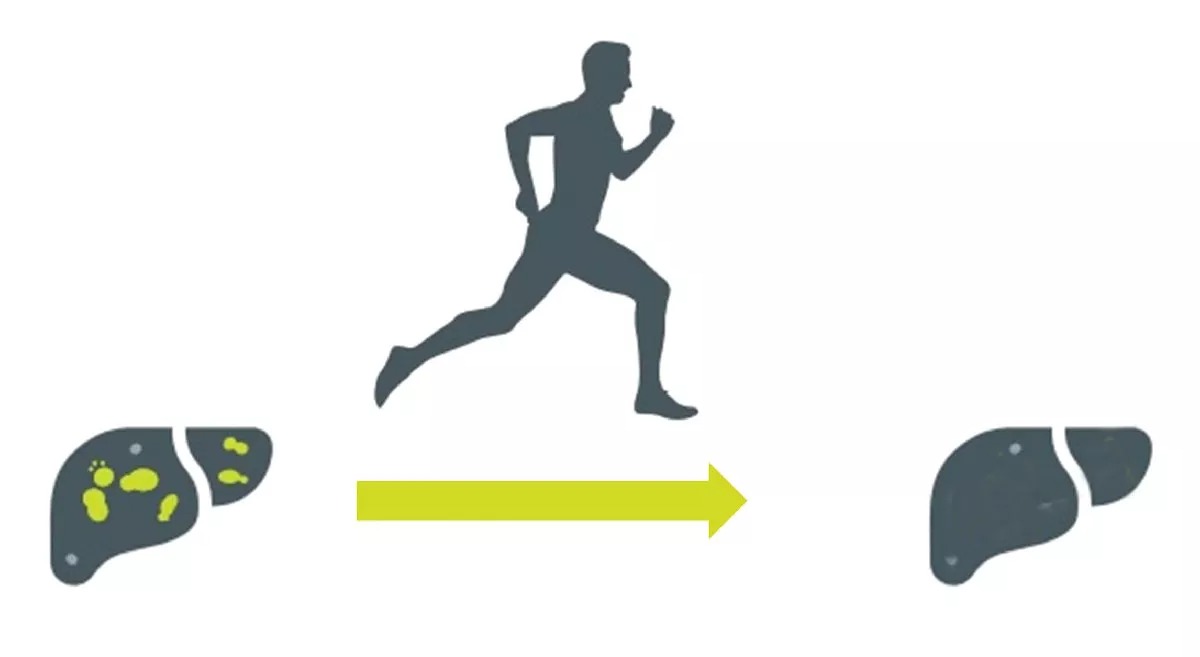
Current recommendations focus on diet and exercise as the first-line treatments for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Specialists suggest a Mediterranean-type diet with plenty of plant foods and healthy fats, coupled with daily physical activity. The goal is a 7-10% weight loss in obese patients, which can dramatically benefit the liver. Exercise guidelines include 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, supplemented with resistance training. Contrary to expectations, a maximum of three cups of coffee per day may also help improve liver function. These changes in lifestyle have been found to decrease liver fat, enhance liver enzymes, and even reverse early liver disease, thus emphasizing their significance in NAFLD management.
Source: American Gastroenterological Association