
Follow WOWNEWS 24x7 on:
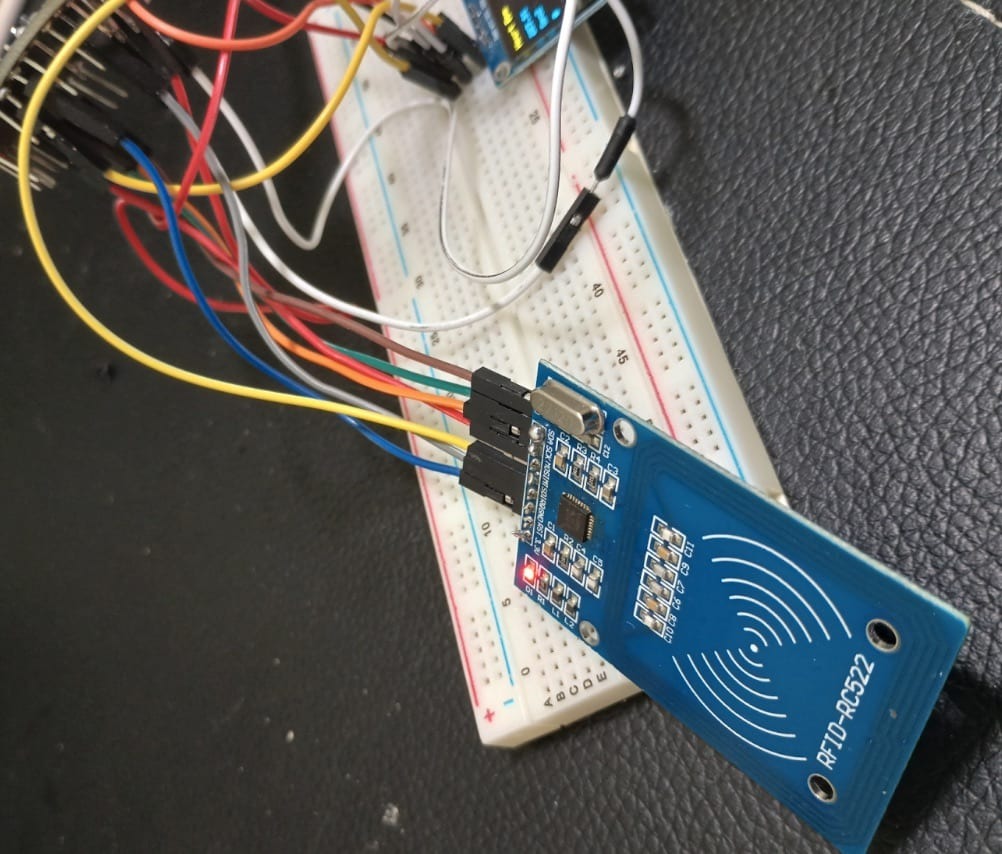
India’s urban mobility is getting a tech-powered makeover. A new IoT-enabled Smart Metro Card System is being prototyped to revolutionize how commuters interact with public transport. Designed to streamline ticketing, reduce human error, and enhance real-time monitoring, this system blends RFID technology with web-based interfaces to create a seamless, contactless travel experience. The project, currently in its pilot phase, is part of India’s broader push toward intelligent transportation under its Smart Cities Mission.
Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the system’s architecture, functionality, and future potential.
1. Core concept and design architecture
- The system is built around RFID-enabled smart cards that store travel credits and commuter data
- Two primary devices are used: one for card recharge and another for entry/exit scanning at metro stations
- Each device is powered by an IndusBoard Coin microcontroller and an RC522 RFID reader/writer module
- The recharge module allows station managers to top up cards using cash payments, while the entry/exit module automatically deducts fare based on travel distance
2. Step-by-step functionality
- Recharge process:
- The commuter hands over their card at the recharge counter
- The RFID reader scans the card and displays the current balance
- The manager inputs the recharge amount, which is written onto the card via the RFID writer
- The updated balance is displayed on a connected screen and stored in the system’s database
- Entry/Exit process:
- At the station gate, the commuter scans the card on the RFID reader
- The system logs the entry time and location, storing it in the backend
- Upon exit, the card is scanned again, and the system calculates the fare based on distance or zones
- The fare is deducted from the card, and the new balance is displayed to both the commuter and station staff
3. IoT integration and real-time monitoring
- The system uses Wi-Fi-enabled microcontrollers to transmit data to a cloud-based server
- Each transaction—recharge, entry, exit—is logged in real time and can be monitored remotely
- A web interface allows station managers to view commuter history, card balances, and system health
- The system supports UUID-based identification, ensuring secure and unique tracking of each card
4. Hardware and software components
- IndusBoard Coin microcontroller: compact, IoT-ready board for handling RFID operations and data transmission
- RC522 RFID reader/writer: used for scanning and updating card data
- Servo motor: controls gate access based on successful scan and balance verification
- Web dashboard: built using HTML and JavaScript, displays transaction logs and card status
- Recharge and scan codes: written in C/C++ using the MFRC522 library, customized for each device’s function
5. Benefits and scalability
- Reduces reliance on manual ticketing and cash handling
- Enables faster commuter flow and shorter wait times at stations
- Enhances transparency and accountability through digital logs
- Can be scaled to integrate with National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) standards
- Offers potential for integration with mobile apps, QR codes, and biometric verification
6. Challenges and future upgrades
- Requires robust cybersecurity protocols to prevent data breaches and card cloning
- Needs consistent internet connectivity for real-time updates
- Future versions may include NFC support, voice alerts, and AI-based fare prediction
- Integration with other transport modes—buses, e-rickshaws, suburban rail—will be key to full adoption
India’s metro systems are evolving from steel-and-concrete corridors into smart, responsive networks. The IoT-enabled Smart Metro Card System is more than a tech upgrade—it’s a blueprint for commuter dignity, efficiency, and digital inclusion. As cities expand and mobility demands grow, such innovations will define the future of urban transport.
Sources: Electronics For You, Metro Rail News, Metro Rail Today


