Image Source: Jagran Josh
Image Source: Jagran Josh
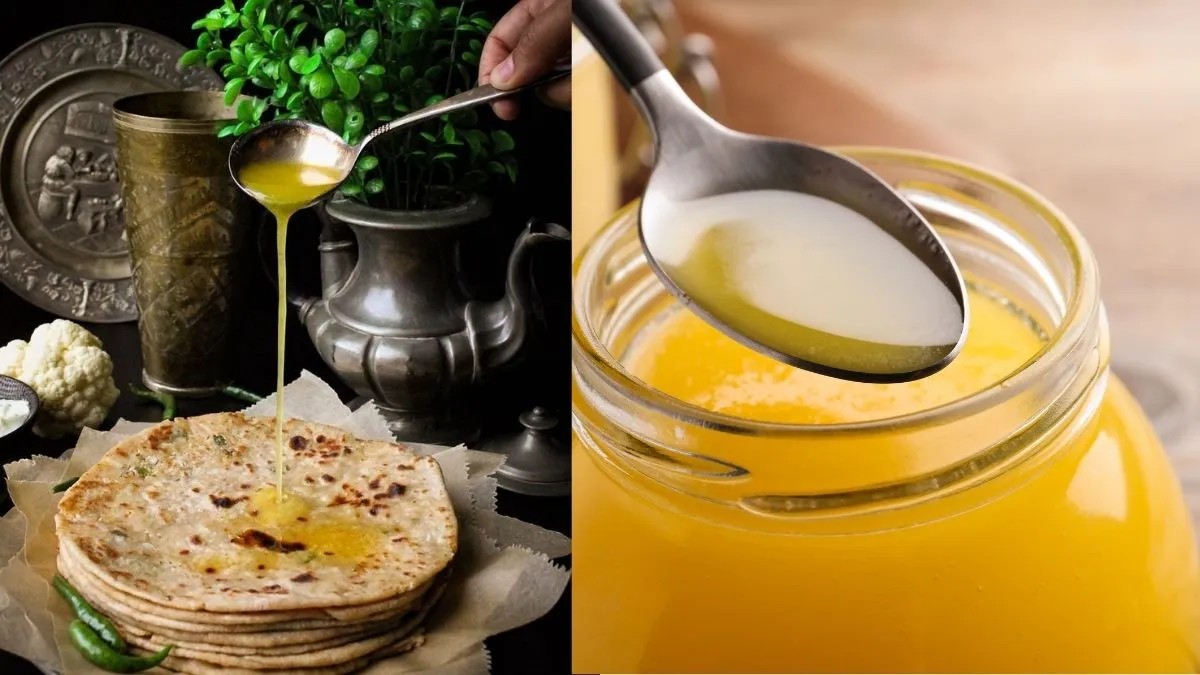
Ghee, a staple in Indian cuisine and tradition, is widely known in English as clarified butter. This golden, aromatic fat is made by simmering butter to remove water and milk solids, leaving behind pure fat with a rich taste and long shelf life. More than just a cooking ingredient, ghee carries deep cultural, religious, and health importance, especially in South Asia, and its recognition worldwide is growing. Today’s report unpacks everything about ghee’s English name, preparation, culinary and medical uses, and the key differences between ghee and regular butter.
Key Insights on Ghee’s English Name and Definition
-
The English term for ghee is clarified butter, a process involving heating butter to remove water content and milk solids.
-
This yields a pure, golden fat that is lactose- and casein-free, making it suitable for those with dairy sensitivities.
-
While people sometimes confuse ghee with regular butter, ghee’s higher smoke point makes it excellent for high-temperature cooking, frying, and sautéing.
Understanding Ghee’s Origins and Language Roots
-
The word ghee derives from the Sanskrit ghṛta, meaning “purified.”
-
It originated in ancient India and has been part of not just culinary traditions but also sacred rituals for thousands of years.
-
Ghee spread to Middle Eastern and other Asian cuisines, each adapting it slightly while maintaining its core role.
Distinguishing Ghee From Butter: What Sets It Apart?
-
Ghee lacks lactose and casein because of the removal process, unlike butter which retains these milk solids.
-
It has a rich, nutty flavor that varies according to the quality of the butter and method of preparation.
-
Its high smoke point (around 250°C) allows cooks to use it for deep frying and high-heat dishes without harmful breakdown, proving healthier than many cooking oils.
Ghee’s Multifaceted Uses in Modern and Traditional Contexts
-
Culinary: A key ingredient in Indian dishes like biryani, sweets such as halwa and laddoos, and everyday meals across regions.
-
Rituals: Used in Hindu pujas for lighting lamps and as a symbol of purity and prosperity.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Embraced in health-conscious diets including keto and paleo due to its vitamin content (A, E, K) and beneficial fatty acids.
-
Medicinal: Valued in Ayurveda for aiding digestion, boosting immunity, and promoting overall wellness.
Nutritional Benefits and Health Considerations
-
Ghee contains fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids like omega-3, omega-6, and butyric acid.
-
Moderated consumption may support heart health and digestive functions.
-
It is gluten-free and considered safer for some with lactose intolerance.
Global Recognition and Varieties of Clarified Butter
-
Although often called clarified butter in English, “ghee” itself is extensively recognized and included in global dictionaries.
-
Different regions have their versions of clarified butter — for example, Korean somin and Turkish Maraş butter — each with unique preparation styles and uses.
-
Ghee brands such as Milkio emphasize grass-fed, high-quality ghee sourced from countries like New Zealand highlighting its international market expansion.
In summary, ghee is more than just clarified butter—the term helps English speakers understand its preparation and dietary qualities, but ghee’s cultural depth and versatility set it apart as a treasured ingredient and health food globally. Whether in Indian kitchens or modern diets abroad, ghee remains a symbol of tradition blending with contemporary nutrition science.
Source: Jagran Josh, Cambridge Dictionary, Wikipedia, Milkio New Zealand
Advertisement
Advertisement