 Image Source: Visual Capitalist
Image Source: Visual Capitalist
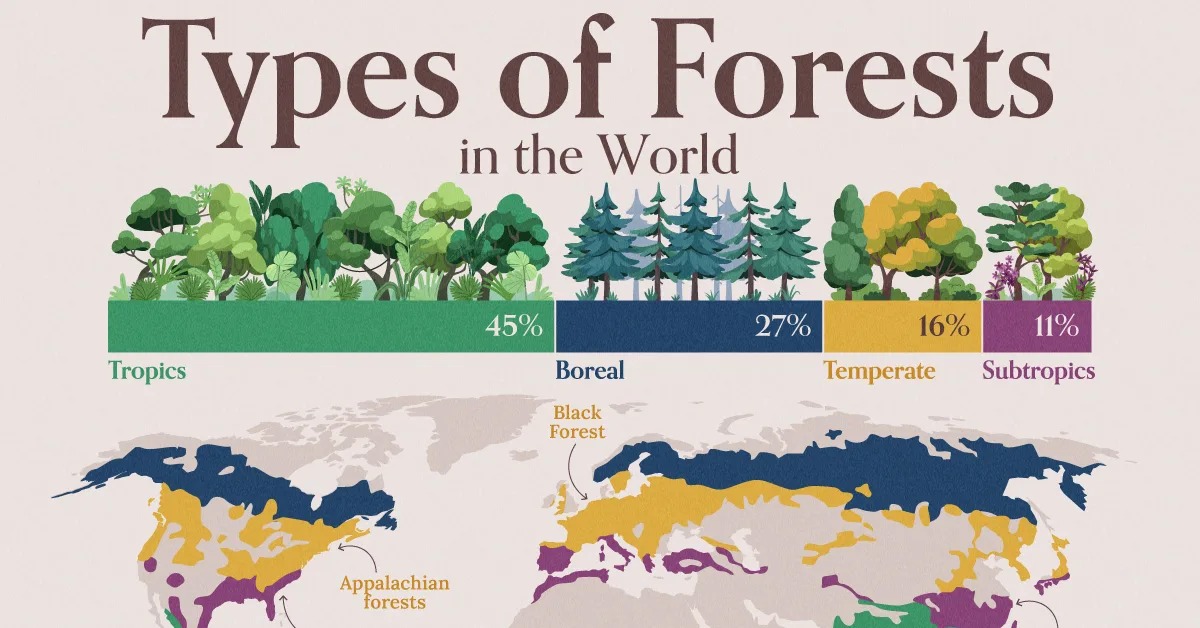
Forests cover nearly one-third of Earth’s land and are classified into four major types—tropical, temperate, boreal, and subtropical. Each type is defined by climate, geography, and biodiversity. Together, they store carbon, regulate climate, and sustain ecosystems, making their protection vital for humanity and the planet.
Show more
Inside the announcement
According to NatureNibble, Earth Reminder, and The Daily Eco, forests are categorized based on rainfall, temperature, and seasonal variations. Tropical forests thrive near the equator with year-round warmth, temperate forests experience four distinct seasons, boreal forests dominate northern latitudes with conifers, and subtropical forests bridge tropical and temperate zones.
Notable updates
Tropical forests: Found in the Amazon and Congo; humid, warm, and biodiversity-rich
Temperate forests: Spread across Europe, North America, and East Asia; marked by four seasons and mixed vegetation
Boreal forests (Taiga): Located in Canada, Russia, and Scandinavia; dominated by conifers and cold climates
Subtropical forests: Present in southern China, India, and South America; transitional ecosystems with diverse species
Global impact: Forests store nearly 296 gigatonnes of carbon and cool the atmosphere significantly
Major takeaway
Mapping the four forest types highlights their ecological importance and diversity. Protecting these ecosystems is critical not only for biodiversity but also for combating climate change and sustaining human livelihoods.
Sources: NatureNibble, Earth Reminder, The Daily Eco
Stay Ahead – Explore Now!
From Tweet to Triumph: How “Dune Machale” Became Zohran Mamdani’s Victory Anthem
Advertisement
Advertisement