AI agents in 2025 are evolving from simple chatbots to autonomous digital coworkers. Building tools for them requires a full-stack approach—combining reasoning engines, APIs, security layers, and monitoring systems. Developers must focus on modularity, scalability, and real-world adaptability to create production-ready agents that can operate across domains and industries.
How to Build Tools for AI Agents in 2025: From Frameworks to Deployment
As AI agents become central to enterprise automation and consumer applications, developers are shifting from prompt engineering to tool-centric architectures. These tools empower agents to perform tasks autonomously—whether booking tickets, analyzing data, or managing workflows. A recent guide by GraffersID and Pragmatic Coders outlines the core components and best practices for building tools that make AI agents truly useful.
Key Highlights from the 2025 Development Landscape:
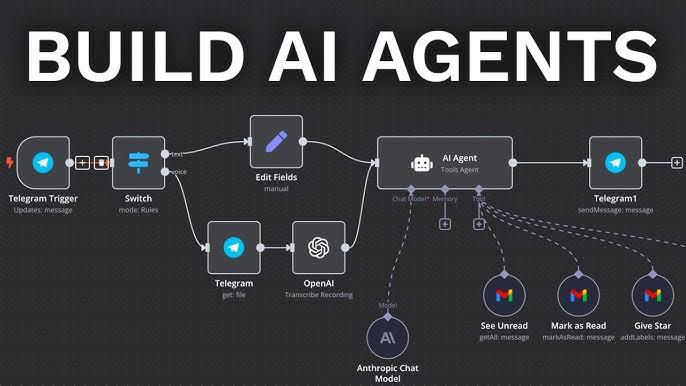
Understanding AI Agent Architecture
Modern agents consist of reasoning modules, memory systems, tool interfaces, and feedback loops.
Tools act as external capabilities—like calculators, web search, or file access—that agents invoke to complete tasks.
Tool Design Principles
Tools should be modular, stateless, and domain-specific.
Each tool must expose a clear API schema, including input/output formats, error handling, and authentication protocols.
Popular Frameworks and Libraries
Developers are using platforms like LangChain, AutoGen, and OpenAgents to orchestrate tool usage.
These frameworks support tool chaining, agent memory, and multi-agent collaboration.
Security and Governance
Tools must include access controls, rate limiting, and audit logs to prevent misuse.
Enterprises are adopting sandboxed environments to test tools before deployment.
Monitoring and Feedback
Real-time dashboards help track tool invocation frequency, success rates, and latency.
Feedback loops allow agents to learn from failed tool calls and improve over time.
Build vs. Buy Decisions
CTOs must weigh the trade-offs between building custom tools and integrating third-party APIs.
Custom tools offer control and flexibility, while external APIs provide speed and scalability.
Use Cases Across Industries
In finance: agents use tools for portfolio analysis and compliance checks.
In healthcare: tools assist with medical record parsing and appointment scheduling.
In retail: agents manage inventory, pricing, and customer support workflows.
Building tools for AI agents is no longer optional—it’s the foundation for creating autonomous, reliable, and scalable digital systems.
Sources: GraffersID, Pragmatic Coders